Keeping the right relative humidity (RH) in your crawl space is one of the most important steps you can take to protect your home. It helps prevent mold, wood rot, pest problems, and even higher energy bills. But what exactly is the right number to aim for?
The Best Relative Humidity for Crawl Spaces
For most areas of a home, the EPA recommends keeping relative humidity between 30 and 50 percent. When it comes to crawl spaces, though, the range shifts a little higher. Because of their location beneath the home and their tendency to hold moisture, the RH in a crawl space should stay below 60 percent, with 45 to 55 percent being ideal.
The EPA says Mold can grow on almost any surface when RH stays above 60 percent for long periods.
Letting the air in your crawl space stay above that mark, especially during the summer, increases the chance of moisture damage and poor indoor air quality. Through a process called the stack effect, humid air and airborne mold particles can rise from the crawl space into your living space.
Why Crawl Space Humidity Rises
Crawl spaces are especially vulnerable during the warmer months. When outdoor air gets pulled into a vented or unsealed crawl space, it cools down quickly. This makes the relative humidity spike, even if the air didn’t feel very humid outside.
That’s why it’s important to understand not just relative humidity, but also dew point. Dew point tells you the exact temperature at which water vapor in the air turns into liquid. If the surfaces under your home are cooler than the dew point of the incoming air, condensation will form.
To dig deeper into how this works, check out our post on Understanding Dew Point in Crawl Spaces (and Why It Matters).
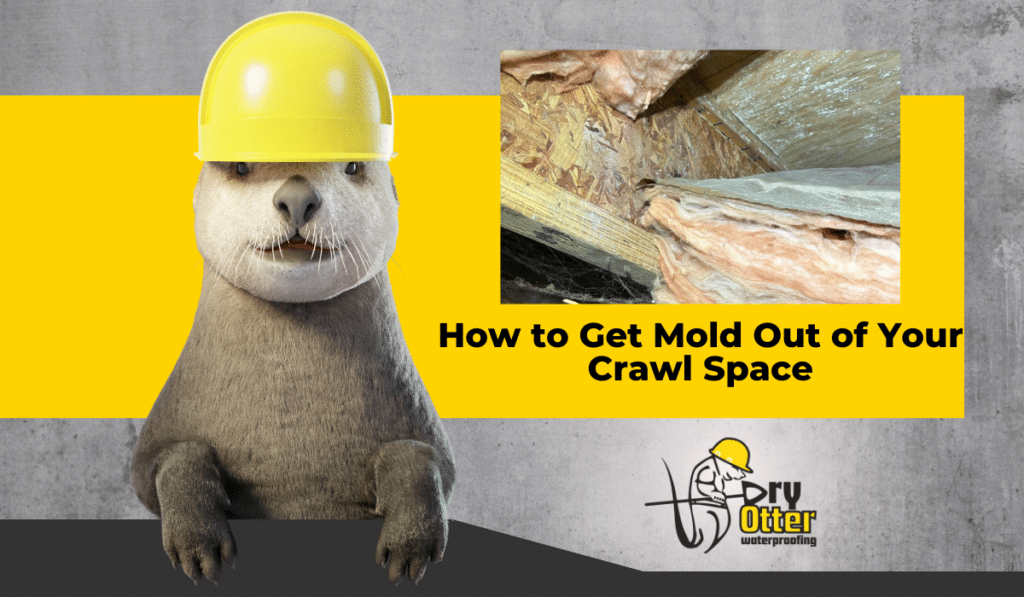
Problems Caused by High Crawl Space Humidity
High humidity in a crawl space can lead to a long list of issues:
- Mold growth and musty odors
- Wood rot and floor system damage
- More insects and wood-destroying pests
- Higher energy bills as HVAC systems work harder
You might also notice signs inside the home, like buckling hardwood floors, condensation on windows, or mold around baseboards. During the summer, these problems tend to get worse. For a seasonal breakdown, read Summer Humidity and Your Crawl Space: What to Know.
How to Lower Humidity in a Crawl Space
To maintain the right RH, consider the following steps:
- Seal crawl space vents and gaps to keep outdoor air out
- Install a thick plastic encapsulation to block ground moisture
- Use a dehumidifier that’s made for crawl spaces and set it to maintain a steady RH
- Make sure the space is properly waterproofed and has a sump pump or drainage system if needed
The U.S. Department of Energy supports this approach. In their Building Technologies research, they recommend sealed and conditioned crawl spaces with vapor barriers as a more effective solution for moisture control and energy efficiency.
Can It Get Too Dry?
When you start to think about it, you might start to wonder if a crawl space get too dry, since there is technically a minimum on the recommended range. While anything is possible, if you have the right kind of dehumidifier installed, such as a commercial Aprilaire dehumidifier, they are designed so that is not a worry. They take into consideration the temperature and dew point of the air. You can read an article we guest wrote for the Aprilaire blog… Crawl Space Dehumidification: Can It Get Too Dry
Keep an Eye on It
Use a simple digital hygrometer to monitor the humidity in your crawl space throughout the year. The RH can change quickly based on outdoor temperatures and weather patterns, so it’s smart to keep tabs on it even if the space looks dry.
Aim for a steady RH between 45 and 55 percent. This level helps prevent problems and gives you peace of mind.
In Summary
Managing crawl space humidity isn’t just a good idea, it’s essential. By keeping the RH in check, you’re protecting your foundation, your home’s air quality, and your long-term repair costs.
Want to see how it all fits together? Visit our Crawl Space Waterproofing Page for a full breakdown of moisture control strategies and how they work.