Basement flooding poses a significant threat to your home and your health. Water is very destructive. Flooding can damage the structural integrity of your home and pose a severe health risk, especially if the water is contaminated with sewage.
Flooding can also cause loss of belongings, mold growth, insurance issues, loss of home value, and mental stress.
Installing a basement sump pump is your best defense against flooding, especially if you live in a flood zone.
What is a Sump Pump & Do I Need One?
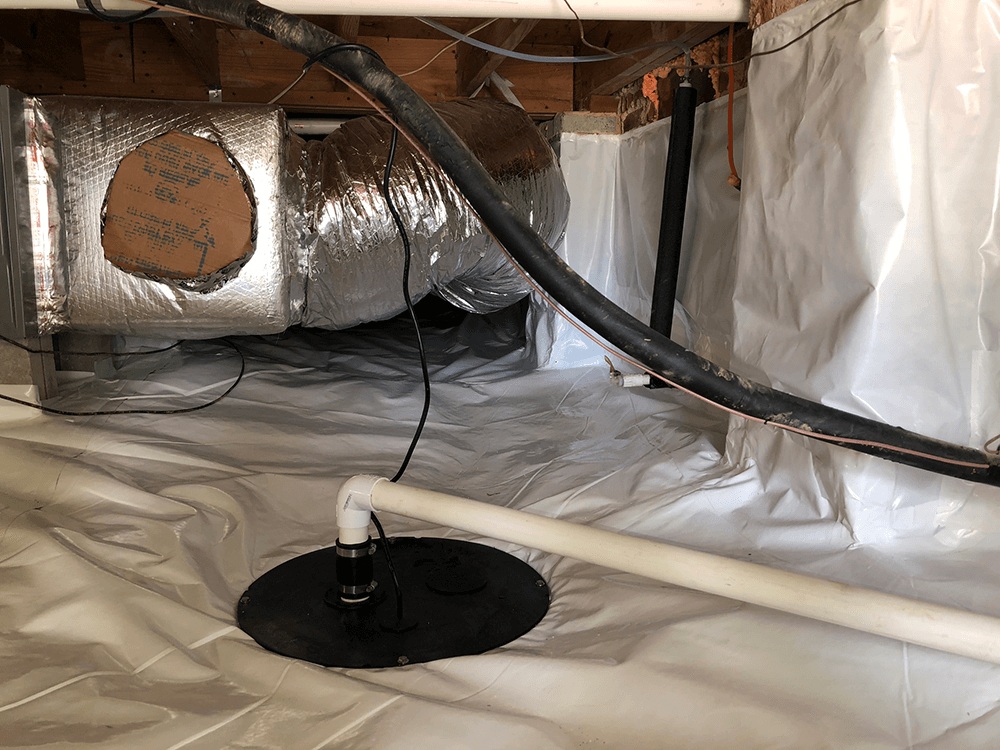

A sump pump is a submersible pump installed in a sump pit, a low point in your basement floor or crawl space. It resembles a cylindrical canister with a motor on top and a pump outlet at the bottom.
How does a sump pump work in a basement?
The sump pit collects water that enters your basement or crawl space. As the water builds in the sump pit, which houses the sump pump, it lifts a float switch inside the basement sump pump.
Once the water reaches a predetermined level, the electrical switch triggers pumping the water outside your home.
Do All Basements Have Them?
No! Not all basements have sump pumps. Here is a breakdown of why some basements do not have sump pumps.
- Low water table: The most crucial factor is the water table, the underground level at which the ground is saturated with water.
If the water table in your area sits well below your basement floor level, there is minimal risk of water seepage, so a sump pump might not be installed.
- Soil type: The soil surrounding your foundation also influences the choice to install a basement sump pump. Soil that is sandy or drains well allows water to move away from your foundation, reducing the risk of flooding.
Clay soils naturally retain water, increasing the likelihood of seepage and requiring a sump pump.
- House construction: If your home is built with a drainage system, like a French drain, water is already set up to drain away from your foundation walls, possibly eliminating the need for a sump pump.
- Basements that are already waterproofed: If a complete waterproofing system with membranes and coatings on the foundation walls has already been installed, this may reduce the need for a basement sump pump.
- Location and age of your home: If your home was built with a drainage system and you live in a dry climate, a sump pump might not be necessary, but if you live in the Charlotte area with high rainfall, a proper system is important. Older homes also probably won’t have an appropriate system of drainage.
The good news is there are signs you may need a sump pump. Our “Problem Signs” quiz will help you assess your specific situation.
How Sump Pumps Work
As we outlined in the beginning, water collects in a sump pit, a low point in your basement floor containing the sump pump.
As water enters the pump, it triggers a float switch. After the water reaches a certain level, the pump starts, removing water from the pit to the outside.
Sump pump components:
- The float switch is the device inside the sump pump that turns it on and off. As the water level rises in the sump pit, the float rises inside the pump, turning it on when it hits the appropriate water level.
- Check valve: This one-way valve prevents water that has been pumped out from flowing back into the sump pit.
- Discharge pipe: The discharge pipe carries the water pumped out of the sump pit away from your home.
- Backup battery: Provides power to the sump pump during a power outage.
- Sump pump alarm: Alerts you if your pump isn’t working correctly.
Types of Sump Pumps-Pedestal vs. Submersible
Pedestal:
This type sits on a base inside the sump pit with the motor positioned above water level.
- Pros: Generally, less expensive, easier to maintain, possibly a longer lifespan, and compact design.
- Cons: They are noisier to operate, they don’t handle solids or debris well, which leads to clogging, and they are less powerful.
Submersible:
Designed to be completely submerged in the water within the sump pit.
- Pros: Quieter, can handle solids and debris better and more powerful.
- Cons: More expensive, requires maintenance, could have a shorter lifespan, and requires a deeper sump pit.
Primary vs. Backup sump pumps
Your primary sump pump is the main source of water removal and operates with electricity. It is triggered by the water level and is important for everyday water removal.
When the primary pump fails, a backup sump pump takes over. It operates with a battery or separate float switch, which kicks in during a power outage or when the water level is so high that another pump is needed.
Beyond the Pump
Maintenance: Test regularly at least once a year, ideally before the rainy season. Pour a bucket of water into the sump pit to trigger the float switch, and make sure the pump turns on and pumps water out.
Periodically clean your sump pump by disconnecting it from the power source, removing it from the pit if possible, and cleaning the inlet screen, removing any debris.
Check for damage, lubricate bearings if applicable, and check the discharge line outside your home to ensure it isn’t clogged.
A basement sump pump is a tool to keep your basement safe and dry, but it isn’t the main solution. To solve your water issues once and for all, basement waterproofing will get to the source of the problem.
Dry Otter offers a wide range of services, including sump pump installation, maintenance, and full basement waterproofing. Look to the professionals to keep your home safe and dry.
Take our “Problem Signs Quiz” for more information. Then, contact Dry Otter for a free inspection to discuss the right plan for you.