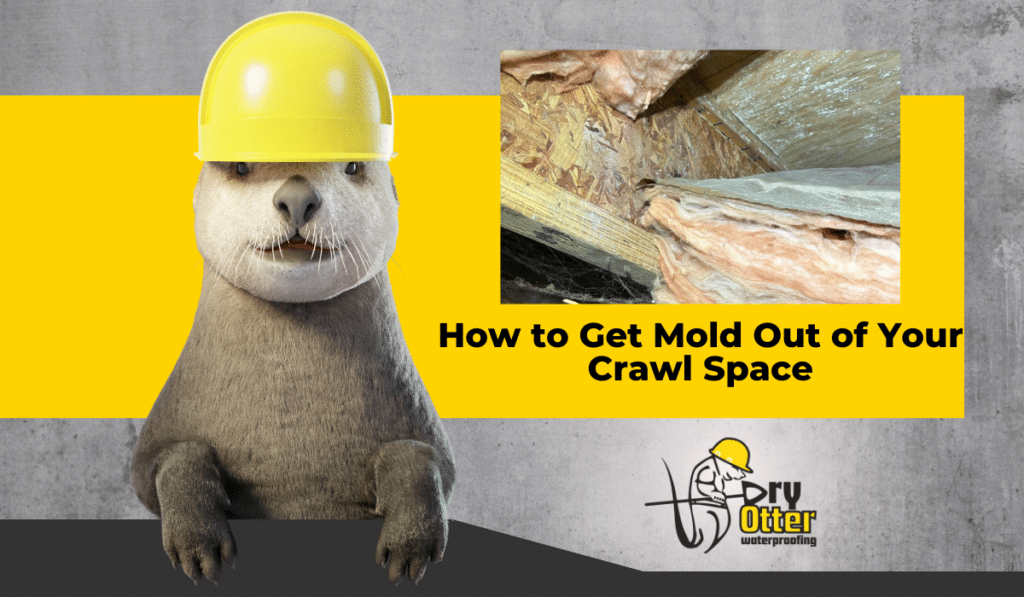
Embarking on a home improvement journey often leads to encountering a myriad of technical terms and concepts. Among these, ‘encapsulation’ stands out as a crucial but sometimes misunderstood term in the realm of building maintenance and crawlspace solutions.
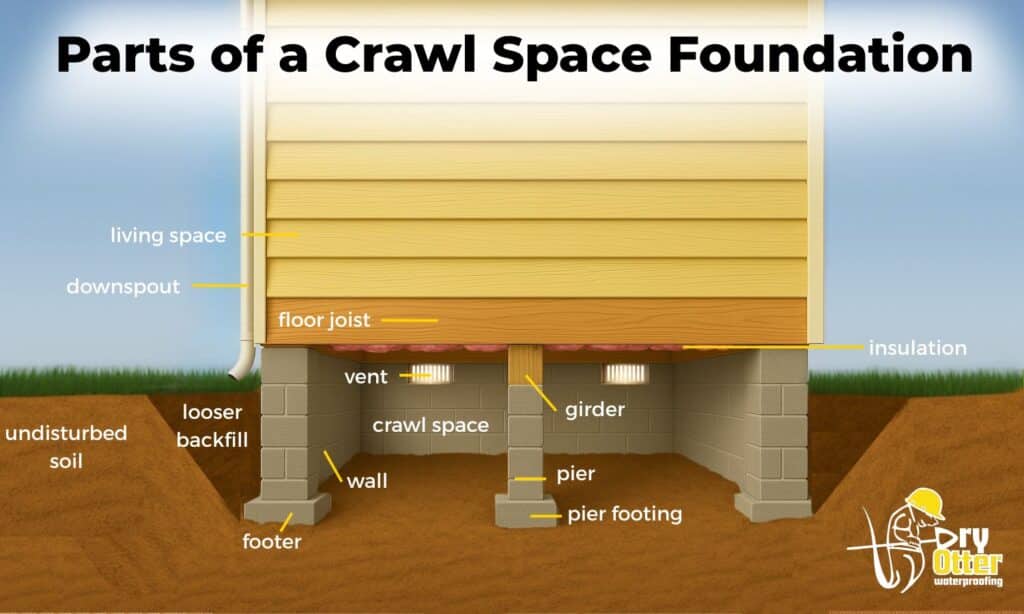
Above the Crawl Space
- Living Space: The finished, inhabited area of the home directly above the crawl space.
- Downspout: A pipe that carries rainwater from the roof gutters down to the ground and ideally away from the foundation to prevent water intrusion.
- Floor Joist: Horizontal wooden structural members that support the floor of the living space above and transfer weight to the girders and walls.
- Insulation: Material placed between or under floor joists to help maintain temperature and reduce energy loss from the living space above.
Within the Crawl Space
- Vent: Openings in the crawl space wall that allow air circulation; these can contribute to moisture issues if not properly managed.
- Crawl Space: The shallow, unfinished space beneath the home used for access to plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems, and where foundation components reside.
- Girder: A large, horizontal support beam that carries the load from floor joists and transfers it to piers or foundation walls.
- Pier: A vertical block structure supporting the girder and floor joists, often spaced throughout the crawl space to provide intermediate support.
- Pier Footing: A concrete pad beneath a pier that distributes the load into the soil below, preventing settling or shifting.
- Wall: The perimeter concrete block or poured concrete structure that encloses the crawl space and supports the home’s outer edges.
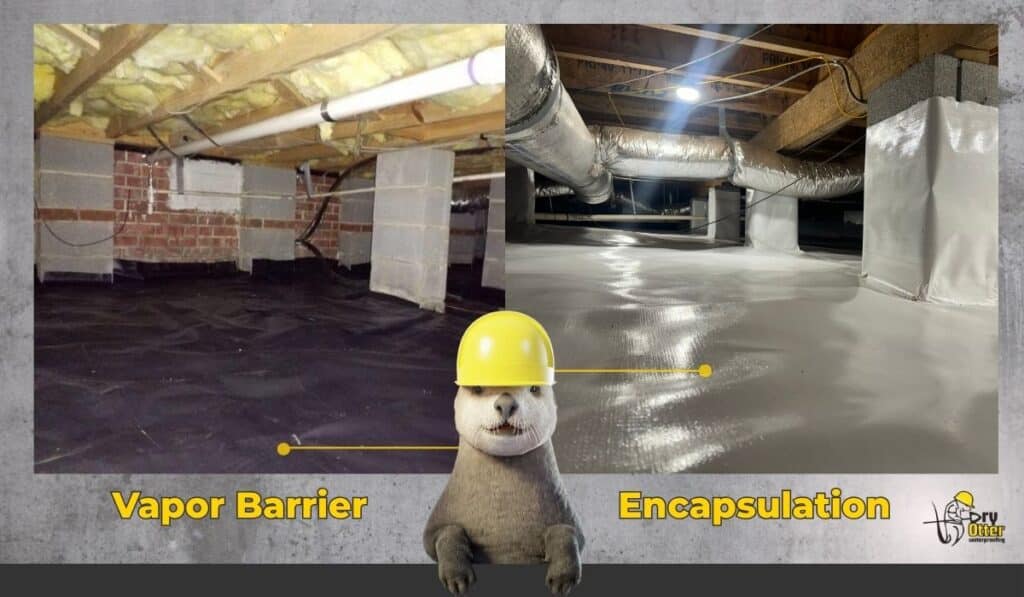
- Vapor Barrier: A plastic or reinforced liner installed on the floor and sometimes walls of the crawl space to block ground moisture from entering the space.
- Encapsulation: The process of sealing the entire crawl space—floor, walls, and sometimes vents—with a vapor barrier and often insulating and conditioning the space to prevent moisture and air infiltration.
- Dehumidifier: A mechanical unit installed in the crawl space (typically after encapsulation) to regulate humidity levels and prevent mold, mildew, and structural damage.

Below the Foundation
- Undisturbed Soil: Natural, untouched soil that hasn’t been excavated or disturbed during construction; it provides more stable support for the foundation.
- Footer (Footing): A wide concrete base at the bottom of the foundation wall or piers that spreads the load over a larger area of soil to prevent sinking.
- Looser Backfill: Soil that was excavated and then replaced around the foundation; less compact and more prone to settling and water intrusion than undisturbed soil.